Overview
Are you intrigued by the concept of machine learning but find yourself daunted by complex theories and techniques? No need to worry - this article has got you covered. It explains the basics of machine learning and guides you in setting up your own machine modeling project.
The article covers several topics:
- What is Machine Learning?
- Types of Machine Learning
- Machine Learning Algorithm examples
- Tips for Setting Up Your Machine Learning Project
What is Machine Learning?
At its core, machine learning is a branch of artificial intelligence that empowers systems to learn and improve from experience without being explicitly programmed. These systems use data to identify patterns, make decisions, and improve their performance over time.
Typically, the goal of machine learning is to develop algorithms that can learn how to perform tasks based on input data. For example, a machine learning model might be trained to predict sales or forecast customer churn based on historical data. Here’s a visualization to illustrate the concept of a basic machine learning model.
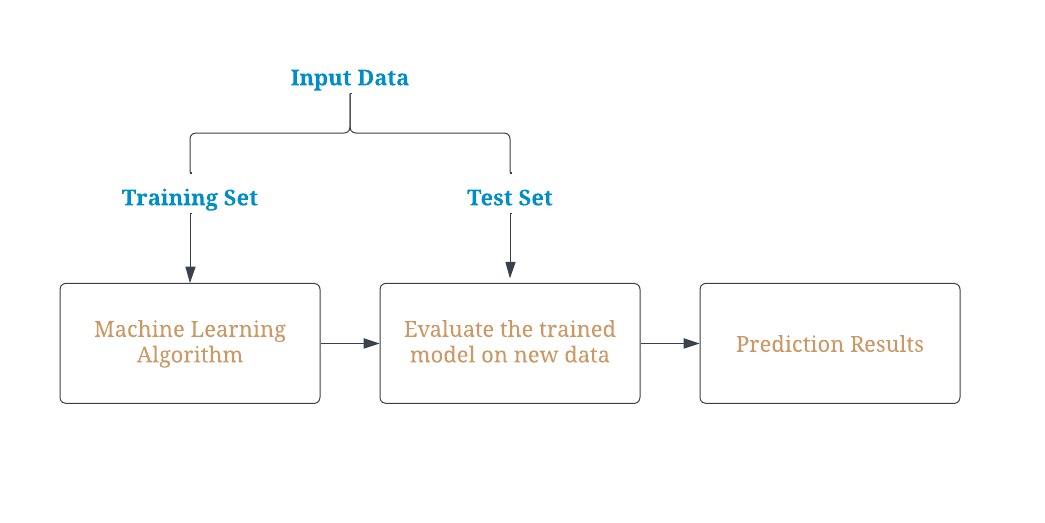
Types of Machine Learning
Machine learning can be categorized into several types, each designed for different data types and objectives. Traditional machine learning (including supervised and unsupervised learning) splits data into a training and testing set to identify patterns and apply them to new data through predictions. Reinforcement learning, on the other hand, does not rely on a predefined dataset but interacts with an environment to learn.
1. Supervised Learning
Supervised learning uses information from a training set to predict a given outcome variable. An algorithm is trained on a labeled dataset, which means that both the input data and the desired output are given. The model learns to map inputs to outputs, ideal for making predictions on unseen data.
Different approaches are classification and regression:
- Classification predicts categorical outcomes, such as labeling students' course feedback as positive or negative.
- Regression predicts continuous outcomes, like forecasting sales of a newly launched product.
If you would like to learn more about supervised learning, you can check out this follow-up article, covering more in-depth theory and (coding) examples: In-depth Introduction to Supervised Machine Learning
2. Unsupervised Learning
Unsupervised learning finds patterns in data without predefined labels or outcomes. If you want to identify relationships in your data, without a given outcome variable, this is the right approach since it deals with unlabeled data. It explores the data’s inherent structure to identify patterns and relationships without explicit guidance or output. Unsupervised learning is often used to group and cluster different objects based on various attributes, such as segmentating customers based on demographics and purchase history.
Different approaches are clustering, generalization and association:
- Clustering can group similar instances together, such as organizing articles into topics based on their content.
- Generalization is used for finding general patterns, like identifying the typical purchasing behavior of different customer segments.
- Association finds rules that represent large parts of the data, for example, discovering that customers who buy bread often also buy cheese.
 Tip
TipLabeled vs. unlabeled data in Machine Learning
Supervised learning makes use of labeled data with predefined tags that direct the model to learn from specified outcomes. Unsupervised learning, on the other hand, uses unlabeled data that does not have these identifiers. Unlabeled data enables the model to find patterns and connections on its own, whereas labeled data simplifies the learning process toward predictable outcomes.
3. Reinforcement Learning
Reinforcement learning teaches a model to make decisions by interacting with its environment. The algorithm receives feedback in the form of rewards or penalties, refining its actions to achieve a specific goal. It is a behavioral modeling technique where the model learns through a trial and error mechanism as it keeps interacting with the environment.
Different approaches are model-based and model-free reinforcement learning:
- Model-based reinforcement learning predicts the outcomes of actions, such as a navigation system learning the fastest route by simulating different paths based on traffic patterns.
- Model-free reinforcement learning learns policies directly from experience without prior knowledge of the model of the environment, such as teaching a computer program to play a video game.
Machine Learning Algorithm examples
Explore the fundamentals of machine learning through a overview of some algorithms and their practical applications.
Supervised Learning Algorithms
-
Linear Regression
- Used for forecasting, linear regression predicts a value based on input features. For example, it can estimate a house’s selling price from its size and location.
-
Logistic Regression
- A classification technique, logistic regression predicts the probability of an instance belonging to a class, like determining if an email is spam or not.
-
Decision Trees
- This algorithm breaks down data by making decisions based on features, useful for tasks like classifying whether a loan should be approved based on financial history.
Unsupervised Learning Algorithms
-
K-Means Clustering
- This algorithm segments data into clusters based on similarity, a common approach for market segmentation by grouping customers according to purchasing habits.
-
Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
- PCA is a technique for dimensionality reduction, helping to simplify data without losing its core information, useful in visualizing high-dimensional data.
-
Apriori Algorithm
- This association rule algorithm is great for discovering relationships between variables in large databases, such as identifying products that frequently get bought together.
Reinforcement Learning Methods
-
Q-Learning
- A model-free algorithm perfect for environments where learning happens through trial and error, such as dynamic advertising where the algorithm learns from user interaction and adjusts which ads to show based on their behavior patterns.
-
Policy Gradients
- This model-free approach directly learns the optimal policy in a continuous environment, such as customizing promotional offers for a streaming service based on subscriber feedback.
Tips for Setting Up Your Machine Learning Project
Starting a machine learning project can seem intimidating, but the right approach can help you. To help you get started, here are some things to keep in mind:
-
Understand your data
- Before you begin modeling, it is essential to get familiar with your dataset. Know what your goals are and find the machine learning approach that fits those goals. It is also very important to clean and preprocess your data to remove noise and irrelevant information.
-
Start simple
- Begin with simple models to establish a baseline performance. Complexity can be added. Start, for example, by training your model on only a few basic variables such as customer demographics.
-
Handling overfitting and underfitting
- Use techniques like regularization to prevent overfitting by penalizing complex models. Also implement cross-validation to make sure your model performs well on unseen data and isn’t just memorizing the training data.
-
Evaluate, iterate and refine
- Depending on your problem, choose appropriate metrics (accuracy, precision, recall, F1-score, RMSE, etc.) to evaluate your model. Model development is an iterative process. Don’t hesitate to refine your models and try different techniques based on performance and insights.
-
Track your process
- Document everything from your data sources, assumptions, model development steps, to performance metrics.
 Summary
SummaryAfter reading this article, you’re good to go to start your own first machine learning project.
You got familiar with:
- Some theory behind machine learning
- The differences between the three types of machine learning
- Some of the most used algorithms and their implementation
- Project management for your own machine learning project
Good luck!



